buildroot 编译环境及流程
Ubuntu环境准备
首先我们需要准备Ubuntu20.04 桌面版。然后安装编译sdk的依赖库
# 更新源
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get upgrade
# 安装编译依赖库
$ sudo apt-get install build-essential subversion git-core libncurses5-dev zlib1g-dev gawk -y
$ sudo apt-get install flex quilt libssl-dev xsltproc libxml-parser-perl mercurial bzr -y
$ sudo apt-get install ecj cvs unzip lib32z1 lib32z1-dev -y
$ sudo apt-get install lib32stdc++6 libstdc++6 libmpc-dev libgmp-dev texinfo -y
$ sudo apt-get install autogen automake autoconf libsocketcan-dev -y
$ sudo apt-get install bison -y
$ sudo apt install python-is-python3 -y
Tina Linux介绍
Tina Linux是全志科技基于Linux内核开发的针对智能硬件类产品的嵌入式软件系统。
Tina Linux中包含Linux系统开发用到的boot 源码、内核源码、驱动、工具、系统中间件与应用程序包。可以方便的定制、编译、打包生成Linux固件镜像。
Tina Linux可以支持构建openWrt和buildroot不同构建系统;也支持单独编译BSP(Board Support Package,板级支持包);能够打包生成固件包,烧录到相应设备中并运行。
SDK软件包的准备
从百度网盘下载源码压缩包,并解压
# 解压Tina SDK,xxx为版本号
$ tar -xzvf zqboard-t113-tina-buildrootxxxxxxxxxx.tar.gz
解压后,会在当前目录下多出来一个TinaSDK5目录,这个就是源码目录了。
解压完成后的完整目录如下:
编译
首先cd到源码根目录
# 如果是在用户根目录下,则执行
cd ~/TinaSDK5
source 一下环境变量
# source 环境变量
source build/envsetup.sh
然后如果是第一次运行,就先彻底清理一下
./build.sh distclean
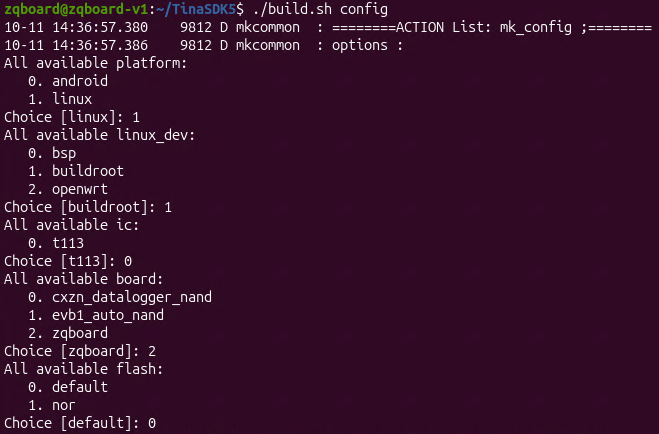
然后载入板子的配置
./build.sh config
然后按照下图选择选项
然后就可以看到配置完成,注意检查中间有没有报错的地方
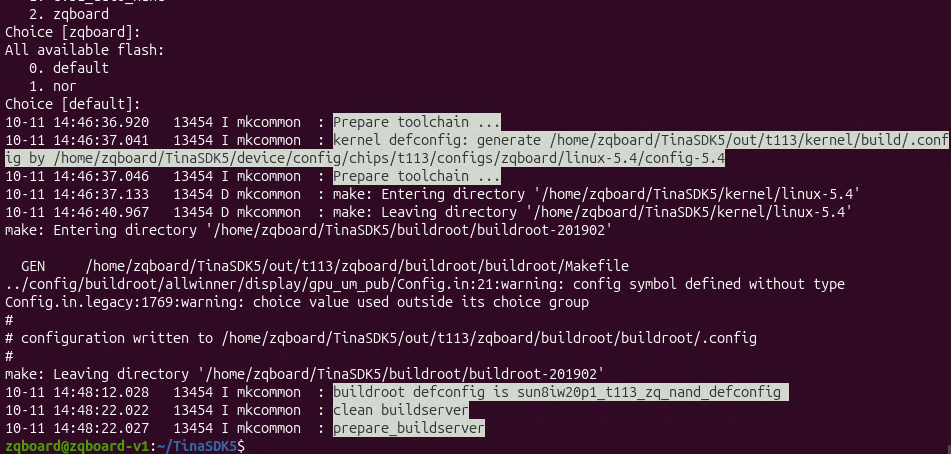
配置完成后,在SDK根目录下会生成一个.buildconfig文件,该文件保存了本次配置的参数。这些配置参数包括内核的编译配置文件、bootloader的编译配置文件、还有buildroot的配置参数(如选择buildroot根文件系统)等,可以通过核对该文件的内容保证配置的正确。
如果你的系统不是网盘里面的预制好的系统的话,需要改一下user.txt和overlay的位置。这两个默认是放到了TinaSDK5的zqboardoverlay文件夹里面了。如果你的用户名不是zqboar,那么运行./build.sh buildroot_menuconfig
然后进入 System Configuration,修改Path to the users tables和Root filesystem overlay directories
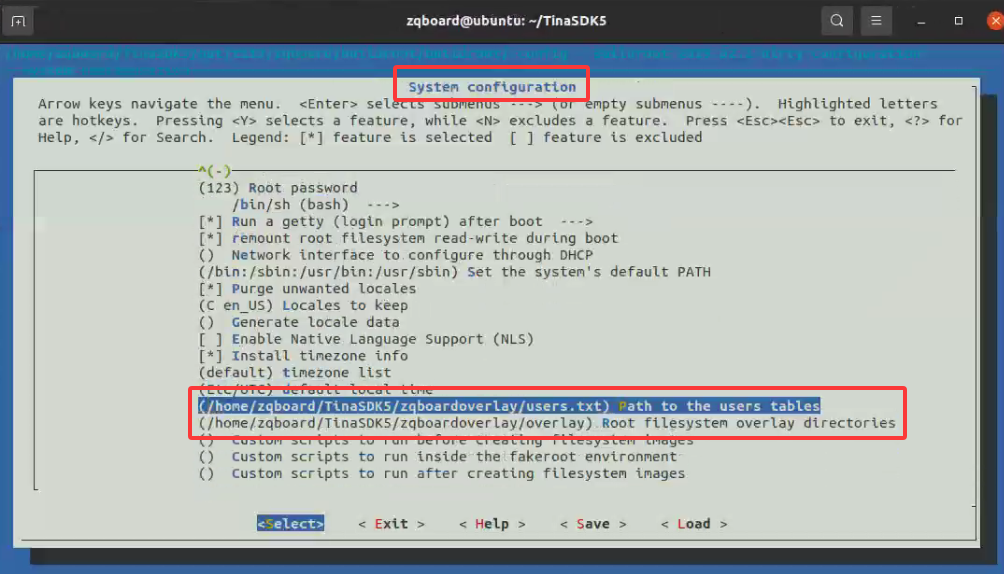
将里面的user.txt和overlay的路径修改正确即可,别忘了保存。
根据实际项目需要,配置完内核选项以及文件系统选项。在LinuxSDK根目录下执行如下命令,可一键编译SPL、U-Boot、Linux内核和文件系统。
./build.sh
编译完成后,输入如下
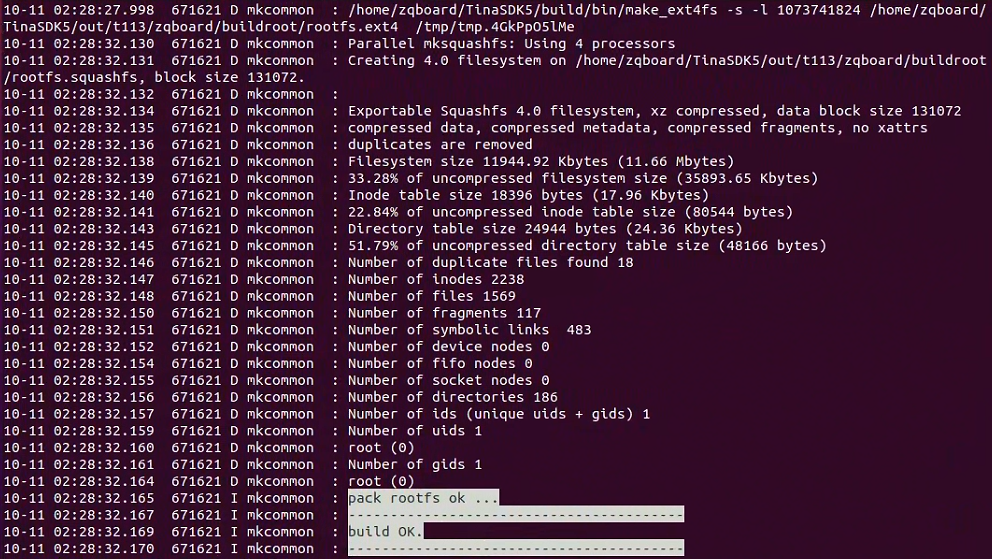
执行如下命令,打包生成Linux系统镜像文件。将新生成的系统镜像固化至核心板即可更新系统。
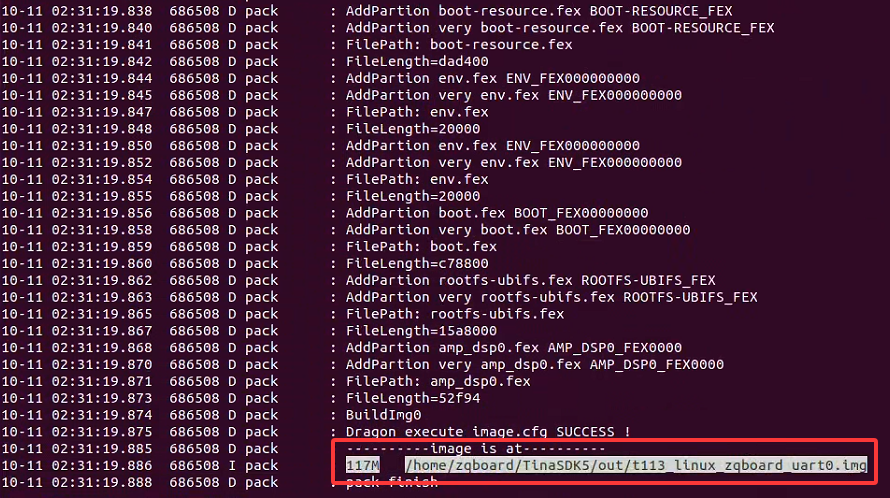
./build.sh pack
打包完成后,我们可以看到打包的文件名称和路径
常用命令
croot / cl - Changes directory to the top of the tree
cbrandy - Changes directory to the brandy
cspl / cboot0 - Changes directory to the spl
csbi[10|14] / copensbi[10|14] - Changes directory to the opensbi
cu / cuboot / cboot - Changes directory to the uboot
cubsp / cubootbsp / cbootbsp - Changes directory to the uboot-bsp
carisc - Changes directory to the arisc
ck / ckernel - Changes directory to the kernel
cbsp - Changes directory to the bsp
cbsptest - Changes directory to the bsptest
cdts - Changes directory to the kernel's dts
cchip / cchips - Changes directory to the chip
cbin - Changes directory to the chip's bin
cboard / cconfigs / cbd - Changes directory to the board
crootfs - Changes directory to the rootfs
cdsp - Changes directory to the dsp
crtos - Changes directory to the rtos
crtoshal / crtos-hal - Changes directory to the rtos-hal
cbuild - Changes directory to the build
cbr - Changes directory to the buildroot
copenssl - Changes directory to the product's openssl-1.0.0
cout - Changes directory to the product's output
ckout / ckernelout - Changes directory to the kernel output
ctarget - Changes directory to the target
chostbin - Changes directory to the hostbin
cplat - Changes directory to the platform
ccommon - Changes directory to the common
Usage: build.sh [args]
build.sh - default build all
build.sh bootloader - only build bootloader
build.sh kernel - only build kernel
build.sh buildroot_rootfs - only build buildroot
build.sh uboot_menuconfig - edit uboot menuconfig
build.sh uboot_saveconfig - save uboot menuconfig
build.sh menuconfig - edit kernel menuconfig
build.sh saveconfig - save kernel menuconfig
build.sh recovery_menuconfig - edit recovery menuconfig
build.sh recovery_saveconfig - save recovery menuconfig
build.sh buildroot_menuconfig - edit buildroot menuconfig
build.sh buildroot_saveconfig - save buildroot menuconfig
build.sh clean - clean all
build.sh distclean - distclean all
build.sh pack - pack firmware
build.sh pack_debug - pack firmware with debug info output to card0
build.sh pack_secure - pack firmware with secureboot
Usage: pack [args]
pack - pack firmware
pack -d - pack firmware with debug info output to card0
pack -s - pack firmware with secureboot
pack -sd - pack firmware with secureboot and debug info output to card0